
DOCTORAL STUDENT, PACO VIRY, JOINS ISA
Funded by the Occitanie Region, the Institute for Sustainable Aviation is stepping up its development and is delighted to welcome Paco VIRY for a thesis
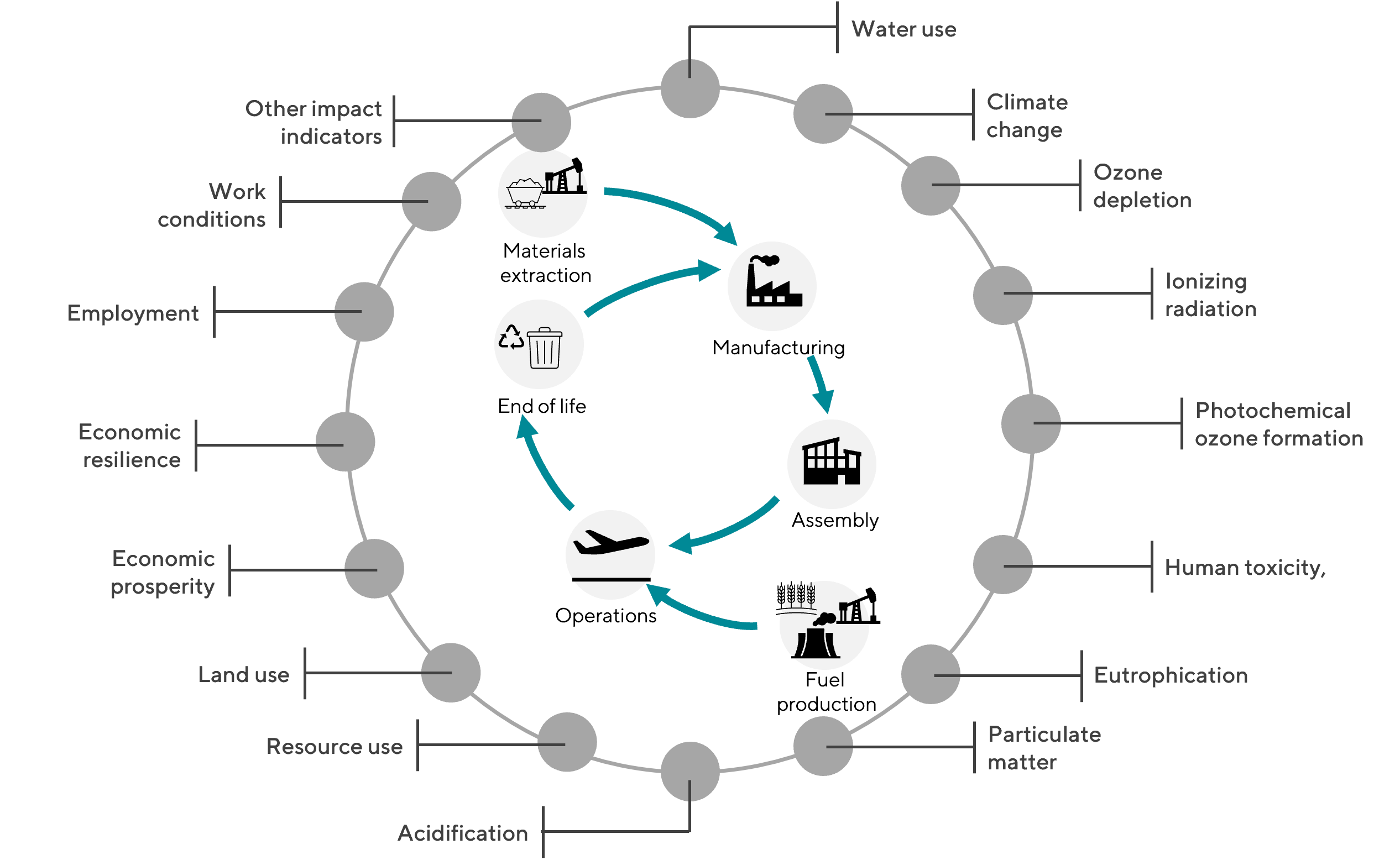
Félix will develop Life Cycle Assessment approaches and integrate them with ISA’s modeling tools to enable systemic exploration of the impacts of tomorrow’s air transport. This approach, extended to a range of environmental indicators, is essential to avoid transferring the climate externality to other externalities, such as mineral resource depletion and land-use change.
Felix’s work will cover different levels of granularity, from the evaluation of new aircraft concepts to their deployment in a global fleet. It will contribute to integrating the concept of absolute sustainability, for the evaluation of aviation transition trajectories, within the AeroMAPS platform supported by ISAE-SUPAERO and the Institute for Sustainable Aviation. Finally, Félix will be undertaking methodological work on the integration of socio-economic indicators into the sector’s life-cycle analysis approaches.
l

Funded by the Occitanie Region, the Institute for Sustainable Aviation is stepping up its development and is delighted to welcome Paco VIRY for a thesis

On March 19, we were delighted to welcome Professor Stef Proost, who presented « An Economist Approach to Sustainable Aviation ».

Invited at the fall edition of the bi-annual IAEG (International Aerospace Environmental Group) meeting by its Chair, Bruno Costes, and our partner Sopra Steria, Laurent